Cottonelle Fresh Feel Flushable Wet Wipes, Adult Wet Wipes, 8 Flip-Top Packs, 42 Wipes Per Pack (336 Total Wipes), Packaging May Vary
41% OffIntroduction
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, commonly known as gallbladder surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to remove the gallbladder. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to laparoscopic cholecystectomy, covering its procedure, benefits, risks, recovery, and more. If you’re considering this procedure or simply interested in learning more, read on to gain a deeper understanding of laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Explained
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located beneath the liver and plays a role in storing bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. When the gallbladder becomes inflamed or develops gallstones, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is often recommended as a treatment option.
Why Choose Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery. The procedure is minimally invasive, resulting in smaller incisions, less scarring, reduced pain, and faster recovery times. Additionally, laparoscopic surgery reduces the risk of complications and allows patients to return to their daily activities sooner.
Preparing for Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Medical Evaluation and Consultation
Before undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy, you will have a medical evaluation and consultation with your surgeon. During this process, your medical history will be reviewed, and you may undergo tests such as blood work, ultrasound, or an abdominal CT scan to assess the condition of your gallbladder.
Dietary Guidelines
Your surgeon will provide specific dietary guidelines to follow in the days leading up to the surgery. These guidelines may include restrictions on solid foods and instructions to consume only clear liquids to prepare your digestive system for the procedure.
Medication Management
It’s important to inform your surgeon about any medications you’re currently taking. They will provide instructions on which medications to continue or discontinue before the surgery. Certain medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be temporarily stopped to reduce the risk of excessive bleeding during the procedure.
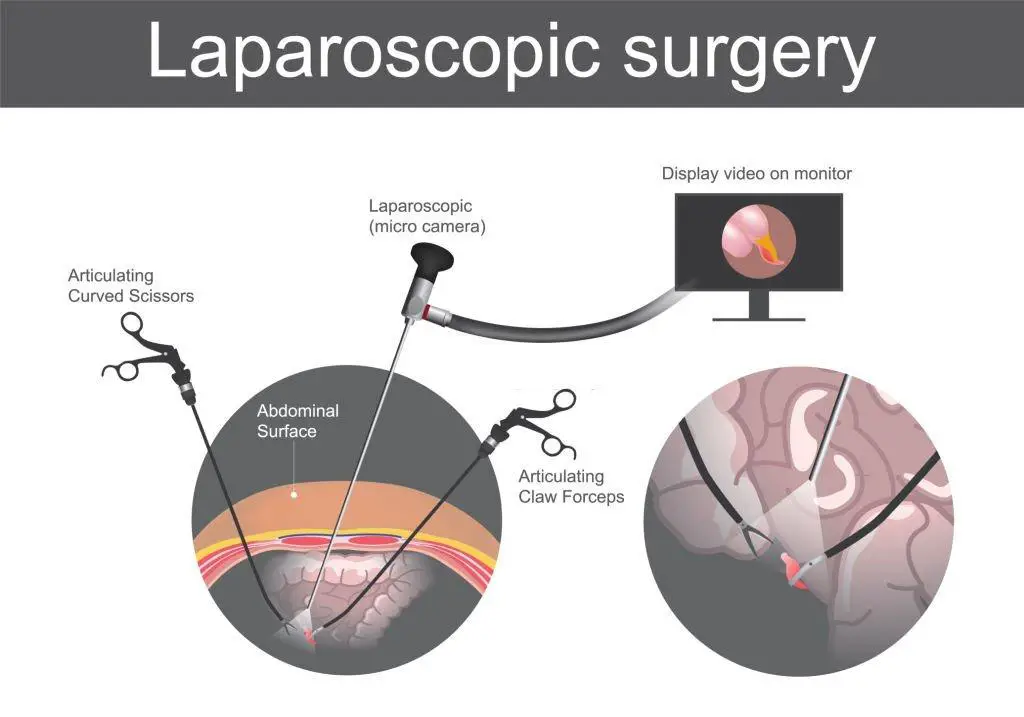
The Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Procedure
Anesthesia Administration
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed under general anesthesia, meaning you will be asleep throughout the procedure. An anesthesiologist will administer the anesthesia and monitor your vital signs during the surgery.
Creating Incisions
The surgeon will make several small incisions in the abdomen, typically measuring less than an inch. These incisions serve as entry points for the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
Inserting the Laparoscope
A laparoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera and light source attached, is inserted through one of the incisions. The laparoscope provides a visual guide for the surgeon, allowing them to navigate and perform the surgery with precision.
Inflating the Abdomen
To create a working space and improve visibility, carbon dioxide gas is pumped into the abdomen after inserting the laparoscope. This inflation lifts the abdominal wall away from the organs, creating more room to maneuver.
Surgical Instrument Insertion
Additional small incisions are made to accommodate the insertion of surgical instruments. These instruments are used to dissect the gallbladder, clip and seal the blood vessels, and remove the gallbladder from the body.
Closing the Incisions
Once the gallbladder has been successfully removed, the surgeon will close the incisions using dissolvable sutures or adhesive strips. Sterile dressings may be applied to protect the incisions as they heal.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, you will be monitored in a recovery room until the effects of anesthesia wear off. Most patients are discharged on the same day as the surgery, but in some cases, an overnight stay may be required for observation.
Pain Management
Pain and discomfort are common after GallBladder Surgery. Your surgeon will prescribe pain medication to help manage any post-operative pain. It’s important to follow the prescribed dosage and inform your surgeon if the pain becomes severe or persistent.
Resuming Activities
While recovery times may vary, most individuals can return to their normal activities within a week or two after the procedure. It’s important to gradually increase your activity level and avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting during the initial stages of recovery.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: How long does a laparoscopic cholecystectomy procedure usually take?
A: On average, a laparoscopic cholecystectomy procedure takes approximately one to two hours. However, the actual duration may vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the case and the surgeon’s experience.
Q: Are there any risks associated with laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
A: Like any surgical procedure, laparoscopic cholecystectomy carries certain risks. These risks may include infection, bleeding, injury to the bile ducts, and anesthesia-related complications. However, the overall risk is relatively low, and serious complications are rare.
Q: Will I experience any dietary restrictions after the surgery?
A: In most cases, patients can resume their normal diet after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. However, it’s common for surgeons to recommend avoiding fatty or greasy foods initially to allow the digestive system to adjust. It’s best to follow your surgeon’s specific dietary guidelines for a smooth recovery.
Q: Can gallstones return after gallbladder removal?
A: Once the gallbladder is removed, gallstones cannot recur. However, in rare cases, small stones may form in the bile ducts. These stones can usually be treated with nonsurgical methods or endoscopic procedures.
Q: Will laparoscopic cholecystectomy leave visible scars?
A: The incisions made during laparoscopic cholecystectomy are small and typically heal with minimal scarring. Over time, the scars will fade and become less noticeable.
Q: Are there alternative treatments to laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
A: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to dissolve gallstones. However, this approach is not always effective, and surgical removal of the gallbladder remains the most common and effective treatment for gallbladder-related conditions.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, or gallbladder surgery, is a safe and effective procedure for treating gallbladder conditions such as inflammation and gallstones. With its minimally invasive nature and faster recovery times, it offers significant benefits to patients. If you’re experiencing gallbladder-related issues, consult with a qualified surgeon to determine if laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the right treatment option for you.
Dr. Ahmed Raza, a renowned gastroenterologist with over 20 years of experience, is the dedicated founder of LifeWithNoGallbladder. With a passion for improving gallbladder health, Dr. Raza shares extensive insights, records, and guidance through his blog, providing individuals with the necessary information to make informed decisions.