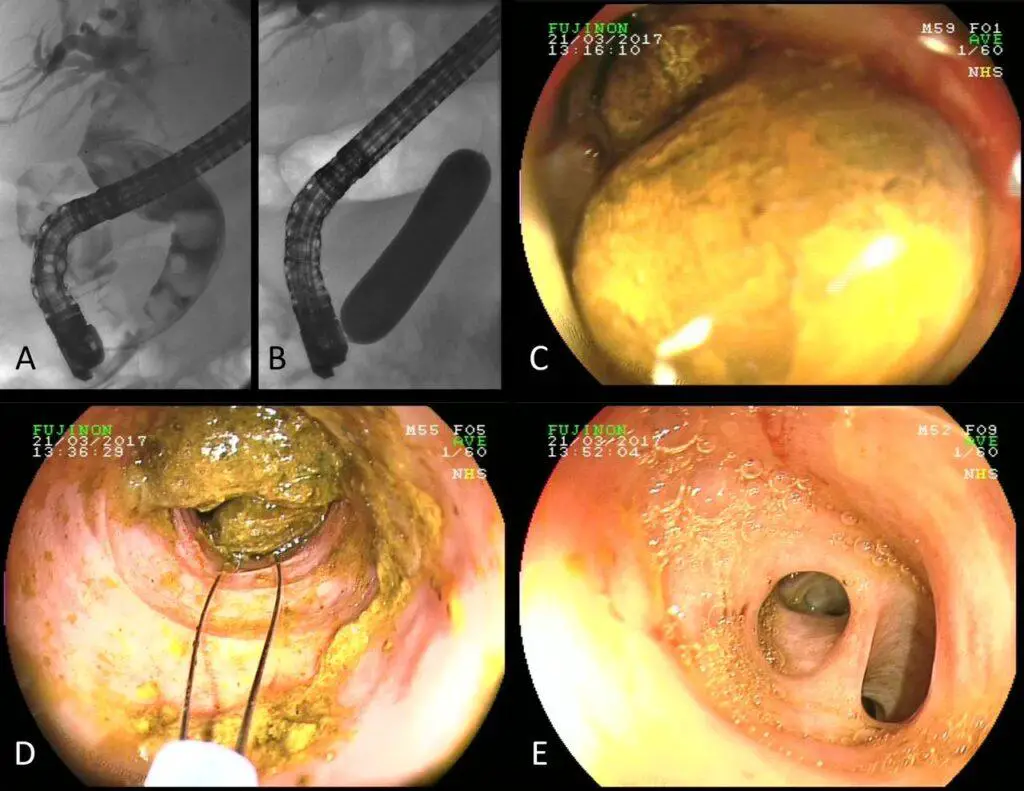
Chronic pancreatitis and bile reflux
Charmin Ultra Soft Cushiony Touch Toilet Paper, 24 Family Mega Rolls = 123 Regular Rolls
4% OffCottonelle Fresh Feel Flushable Wet Wipes, Adult Wet Wipes, 8 Flip-Top Packs, 42 Wipes Per Pack (336 Total Wipes), Packaging May Vary 4.7 out of 5 stars(127420) 24% Off $15.79 ($0.05 / Count) $12.00 ($0.04 / Count) (as of April 17, 2024 08:50 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of …
Chronic pancreatitis and bile reflux Read More »