Safety 1st Deluxe 25-Piece Baby Healthcare and Grooming Kit (Arctic Blue)
$21.74 (as of April 26, 2024 11:13 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Introduction:
Gastritis and gallbladder conditions are two wonderful fitness issues that could reason abdominal discomfort and digestive problems. Even as they percentage a few similarities in signs, it’s important to apprehend their differences to make sure correct prognosis and suitable treatment. In this newsletter, we will delve into the key aspects of gastritis and gallbladder conditions, highlighting their symptoms, reasons, and treatment options. By gaining higher information on these conditions, you can take proactive steps toward preserving your digestive fitness.
A brief explanation of gastritis and gallbladder conditions
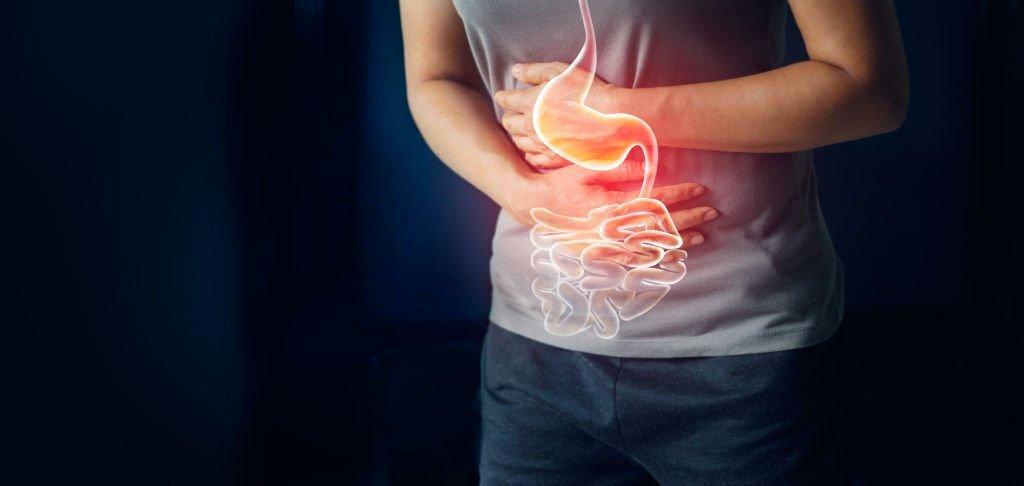
Gastritis refers to the infection of the belly lining, that may occur due to various factors inclusive of bacterial infections, prolonged use of sure medicinal drugs, excessive alcohol intake, or continual pressure. The infection can cause symptoms like stomach aches, nausea, vomiting, and a sense of fullness.
However, the gallbladder is a small organ positioned under the liver that aids in digestion by storing bile produced by the liver. Gallbladder situations usually encompass gallstones, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), or gallbladder dysfunction. These situations can reason severe aches in the higher stomach, especially after ingesting fatty or greasy meals.
Importance of understanding the differences
Distinguishing between gastritis and gallbladder situations is critical for accurate Diagnosis and powerful remedies. Although each situation might also happen with similar signs and symptoms such as abdominal pain, the underlying reasons and remedy tactics vary substantially. Misdiagnosis or mistreatment can lead to extended suffering and capacity complications. Therefore, comprehensive expertise in the nuances of gastritis and gallbladder conditions empowers individuals to be looking for suitable scientific interests and take essential steps toward recuperation.
Understanding Gastritis
Definition and Explanation:
What is Gastritis? Gastritis is a general term for a condition characterized using inflammation of the stomach lining, known as the gastric mucosa. The infection can disrupt the regular functioning of the belly, leading to various symptoms and pain.
Causes and risk factors:
- Gastritis can be caused by several factors, such as:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. Pylori) contamination
- extended the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- excessive alcohol intake
- chronic strain
- Autoimmune problems
Signs and symptoms:
Common symptoms of Gastritis:
Gastritis can present with numerous signs and symptoms, along with:
- Abdominal pain or pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating and a sense of fullness
- Loss of urge for food
- Heartburn or acid reflux
- Indigestion
- Blood inside the stool or vomit (in severe cases)
Severity and duration of signs: The severity and duration of signs can vary depending on the underlying motive and kind of gastritis. Acute gastritis symptoms can be severe but commonly remedied inside a quick length as soon as the reason is addressed. Chronic gastritis symptoms can persist for a prolonged period and might differ in depth.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic methods for Gastritis:
To diagnose gastritis, scientific professionals might also appoint several strategies, which include:
Medical records assessment: evaluating signs, medical heritage, and hazard factors.
Physical examinations: Assessing belly tenderness, bloating, or other symptoms.
Laboratory checks: Blood exams to stumble on H. Pylori contamination or assess irritation levels.
Stool exams: examining stool samples for symptoms of blood or contamination.
Endoscopy: inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the belly to visualize the lining and accumulate biopsy samples.
The role of clinical professionals in diagnosis: clinical experts, which include gastroenterologists, play an essential function in diagnosing gastritis. They interpret signs, order relevant exams, and examine the outcomes to determine the type and severity of gastritis. Their know-how guarantees accurate diagnosis and suitable remedy suggestions.
Treatment Options:
Lifestyle and nutritional adjustments: Adopting a healthful weight-reduction plan and making way-of-life adjustments can be considerably useful resources in coping with gastritis. Key considerations include:
Importance of a healthful food regimen:
- Emphasizing entire foods, fruits, veggies, and lean proteins.
- Foods to keep away from highly spiced, acidic, fatty, and fried foods, in addition to caffeine and carbonated beverages.
- Ingredients to include: high-fiber foods, probiotics, and meals rich in antioxidants.
- The role of alcohol and smoking cessation: avoiding or minimizing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking, as they can worsen gastritis signs and symptoms.
Medicinal drugs: scientific specialists might also prescribe medicinal drugs to alleviate gastritis signs and symptoms and deal with underlying causes. Not unusual medications consist of:
- Antacids: Neutralize belly acid to offer brief relief.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): reduce stomach acid production to promote recuperation.
- Medications: Prescribed in instances of H. Pylori infection to eliminate the microorganism.
Cytoprotective agents: help guard the stomach lining from damage.
- Alternative and Complementary treatment options: while herbal remedies and complementary treatment options may also provide symptom relief, it is vital to consult a healthcare expert before attempting them. A few alternatives include:
- Natural remedies and dietary supplements: together with ginger, chamomile, or probiotics.
- Herbal remedies: Examples consist of licorice root, aloe Vera, or slippery elm.
The significance of consulting a healthcare professional: To make sure safety, effectiveness, and suitable integration with traditional remedies.
Expertise in gastritis, its signs and symptoms, prognosis techniques, and remedy options empowers people to actively manipulate their condition. It’s miles vital to discuss carefully with healthcare experts to obtain an accurate diagnosis and develop a tailored treatment plan for most excellent gastritis management.
Understanding Gallbladder Issues
Definition and explanation:
What is the gallbladder?
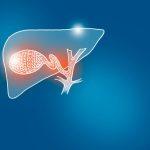
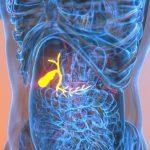
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ placed under the liver. Its number one characteristic is to store and concentrate bile, a substance produced using the liver that aids in the digestion of fats.
Common conditions affecting the gallbladder:
The gallbladder can be laid low in various situations, which include:
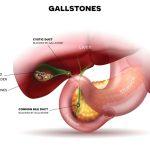
Gallstones: Hardened deposits that form within the gallbladder due to imbalances in bile composition.
Cholecystitis: infection of the gallbladder, often as a result of gallstones.
Gallbladder dysfunction: Refers to impaired gallbladder emptying or bizarre contractions.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Several factors contribute to gallbladder troubles, which include:
Gallstones: Imbalances in bile composition, inclusive of high cholesterol or bilirubin ranges.
Weight problems: extra body weight can grow the threat of gallstone formation.
Gender and age: ladies are extra prone to gallstones, specifically in the course of pregnancy or after menopause.
Fast weight loss: dropping weight too fast can promote gallstone formation.
Genetic factors: own family history of gallbladder problems might also grow the danger.
Signs and symptoms:
Normal signs and symptoms of Gallbladder problems: Gallbladder issues regularly appear with the subsequent symptoms:
- Abdominal ache, usually in the top proper quadrant or mid-stomach
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating and gasoline
- Indigestion or heartburn
- returned or shoulder pain
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) in intense cases
Identifying Acute as opposed to chronic problems: Acute gallbladder troubles, together with acute cholecystitis or biliary colic, occur abruptly and are generally characterized using severe, intermittent aches. Continual gallbladder problems, which include chronic cholecystitis or gallstone headaches, can also exhibit milder, recurrent signs over a prolonged duration.
Spotting the symptoms of Gallstones and Gallbladder infection: Gallstones can purpose signs and symptoms like sudden and intense aches (biliary colic) after they impede the bile ducts. Infection of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) can bring about persistent pain, tenderness in the abdomen, fever, and a multiplied white blood cellular count number.
Diagnosis:
Diagnostic techniques for Gallbladder situations: Diagnosing gallbladder troubles may contain the following techniques:
Scientific history evaluation: evaluating signs, chance factors, and circle of relatives records.
Bodily examinations: Palpating the stomach for tenderness or swelling.
Imaging checks: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the gallbladder and stumble on abnormalities.
Blood assessments: Assessing liver characteristics and checking for signs and symptoms of infection or infection.
Medical assessments and tactics involved: specialists, which include gastroenterologists or surgeons, may conduct specific assessments, together with:
Stomach ultrasound: to visualize the gallbladder and identify gallstones or infections.
Cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan): Evaluate gallbladder features and bile and go with the flow.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): allows visualization and diagnosis of bile duct abnormalities.
A session with experts: Consulting with gastroenterologists or surgeons is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment tips for gallbladder problems. Those professionals have expertise in managing gallbladder conditions and may guide patients via the diagnostic process.
Treatment options:
Medicinal drugs: medications may be used to manage gallbladder problems, particularly for symptomatic remedy and dissolution of gallstones. Common medications encompass:
Oral bile acid tablets: useful resource in dissolving positive styles of gallstones.
Analgesics: help alleviate aches associated with gallbladder issues.
Non-Surgical Interventions: Non-surgical techniques intended to control symptoms and sell gallbladder health through lifestyle and nutritional modifications, together with:
Nutritional changes: Avoid fatty or greasy foods, ingest a balanced weight-reduction plan, and eat smaller, more frequent food.
Lifestyle adjustments: retaining a healthy weight, everyday exercising, and managing pressure.
Pain management strategies: making use of warm pads, using over-the-counter ache relievers, or trying relaxation techniques to relieve pain.
Surgical Interventions: surgery may be necessary for sure gallbladder situations, which include gallstones or excessive cholecystitis. The maximum not unusual surgical procedure is laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which includes removing the gallbladder through small incisions. The benefits of this manner encompass minimum scarring and shorter recovery time.
Potential dangers and complications: Surgical interventions, even though usually safe, can deliver some dangers, such as contamination, bleeding, bile duct damage, or complications related to anesthesia. It is important to talk about capacity dangers and benefits with the healthcare issuer earlier than the present process of any surgical procedure.
Expertise in gallbladder troubles, their signs and symptoms, diagnostic methods, and remedy alternatives empower individuals to make knowledgeable choices concerning their healthcare. Consulting with professionals and following their guidance guarantees accurate analysis and appropriate control of gallbladder conditions.
Gastritis vs. Gallbladder: Key differences
Signs comparison:
Overlapping symptoms among Gastritis and Gallbladder conditions: Gastritis and gallbladder troubles can proportion some similar signs, along with:
- abdominal ache or pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating and indigestion
Particular signs and symptoms unique to every condition: Gastritis:
- Burning sensation or heartburn
- loss of urge for food
- The feeling of fullness after eating small quantities
- Black, tarry stools (indicating bleeding inside the stomach)
Gallbladder situations:
- intense, cramping ache inside the top right abdomen or mid-stomach (gallstone-related ache)
- ache to radiate to the lower back or shoulder
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) in excessive instances
Diagnostic variations:
How scientific specialists Differentiate between Gastritis and Gallbladder troubles: medical professionals employ diverse diagnostic techniques to distinguish between gastritis and gallbladder conditions, such as:
Detailed clinical history assessment: identifying precise symptoms, threat elements, and styles.
Physical examinations: Assessing belly tenderness, presence of jaundice, or other relevant signs.
Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the gallbladder and belly lining.
Endoscopy: inserting a bendy tube with a digicam to look at the belly lining and accumulate biopsy samples.
Laboratory checks: Blood exams to check for markers of irritation, H. Pylori infection, liver characteristic, and bile duct abnormalities.
Unique checks and Markers utilized in Diagnosis: Gastritis:
Endoscopy with biopsy: permits direct visualization of the stomach lining and collection of tissue samples for evaluation.
Blood assessments: check for H. Pylori contamination, ranges of infection markers, and specific antibodies.
Gallbladder conditions:
Ultrasound: Visualizes the gallbladder for the presence of gallstones or inflammation.
Cholescintigraphy (HIDA test): Evaluates gallbladder function and bile drift.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): Assists in diagnosing bile duct abnormalities.
Treatment Approaches:
Wonderful treatment alternatives for Gastritis and Gallbladder conditions:
Medicines: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce stomach acid, antibiotics for H. Pylori eradication, and cytoprotective agents to defend the stomach lining.
Lifestyle modifications: nutritional changes (averting trigger ingredients, lowering alcohol intake), strain reduction strategies, and smoking cessation.
Gallbladder conditions:
Medicines: pain management medications, oral bile acid drugs to dissolve positive kinds of gallstones.
Non-surgical interventions: nutritional adjustments (low-fat weight loss program), lifestyle changes (weight control, exercise), and pain control strategies.
Surgical interventions: elimination of the gallbladder via laparoscopic cholecystectomy in instances of gallstones or severe inflammation.
Why accurate Diagnosis is critical for effective remedy: Accurate Diagnosis is important due to the fact gastritis and gallbladder situations require distinctive remedy methods. Misdiagnosis or mistreatment can result in prolonged suffering, unresolved signs and symptoms, and capability complications. Every condition has its very own set of reasons and underlying mechanisms, necessitating focused interventions for the most desirable results. Therefore, obtaining a correct diagnosis ensures that suitable remedies are implemented, leading to powerful symptom remedies and improved basic fitness.
Information on the key differences in signs, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options between gastritis and gallbladder situations is important for accurate analysis and ultimate control. Looking for scientific attention from healthcare experts is important to decide the specific condition and increase an individualized remedy plan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Here are answers to some generally asked questions about gastritis and gallbladder situations:
Q1. Can gastritis and gallbladder issues have comparable symptoms?
Yes, gastritis and gallbladder situations can share some overlapping signs and symptoms, together with abdominal aches, nausea, and bloating. But, there also are particular symptoms specific to every circumstance which could assist differentiate between them.
Q2. How are gastritis and gallbladder troubles identified?
Diagnosis usually entails a combination of medical history assessment, physical examinations, imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan), endoscopy, and laboratory exams (blood assessments, stool assessments). Consultation with clinical experts, inclusive of gastroenterologists or surgeons, is vital for accurate analysis.
Q3. What are the remedy alternatives for gastritis and gallbladder situations?
The treatment options differ for every circumstance. Gastritis may be controlled with medicines like proton pump inhibitors, antibiotics, and lifestyle adjustments along with dietary adjustments and pressure reduction.
Conclusion:
In the end, understanding the variations between gastritis and gallbladder conditions is crucial for correct analysis and appropriate remedy. Gastritis entails irritation of the stomach lining, at the same time as gallbladder conditions affect the gallbladder, frequently because of gallstones or inflammation. Spotting particular signs and symptoms, diagnostic techniques, and treatment alternatives for each circumstance is critical for powerful control.
In search of scientific recommendations and consulting with healthcare specialists is essential for acquiring a correct analysis and developing a tailor-made remedy plan. Early intervention and the right management of gastritis and gallbladder conditions can assist alleviate symptoms, save you headaches, and improve general digestive health.
Taking proactive steps toward preserving digestive health can make contribute to a long-time period nicely-being and a better quality of life.
Recall, if you are experiencing signs or have worries about your digestive fitness, it’s far usually best to seek advice from a healthcare professional for personalized advice and steerage
Dr. Ahmed Raza, a renowned gastroenterologist with over 20 years of experience, is the dedicated founder of LifeWithNoGallbladder. With a passion for improving gallbladder health, Dr. Raza shares extensive insights, records, and guidance through his blog, providing individuals with the necessary information to make informed decisions.