Tylenol Infants Liquid Pain Relief & Fever Medicine, Oral Suspension, Acetaminophen for Sore Throat, Headache & Teething, Pain Reliever & Fever Reducer for Kids; Cherry Flavor, 2 Fl. Oz.; Pack of 1
23% OffGallstones are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. These small, hardened deposits can form in the gallbladder, causing pain and discomfort. Unfortunately, there are several myths and misconceptions surrounding gallstones that can lead to confusion and misinformation. In this article, we will debunk some of the most prevalent myths about gallstones to provide you with accurate information and help you make informed decisions about your health.
Introduction: Understanding Gallstones
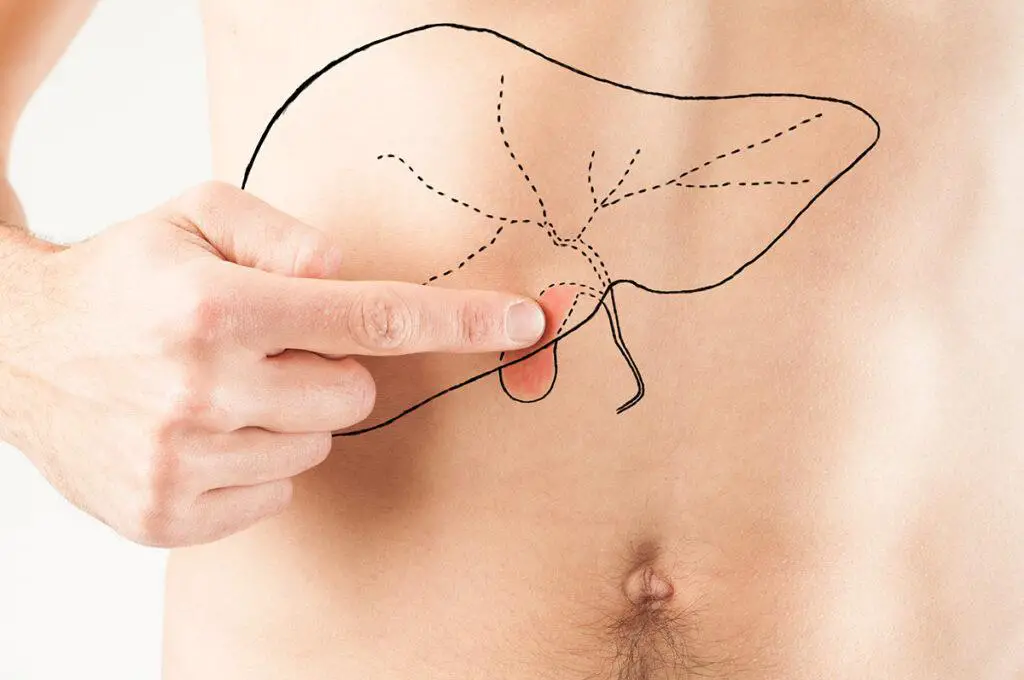
Before we dive into the myths, let’s briefly understand what gallstones are. Gallstones are solid deposits that develop in the gallbladder, a small organ located below the liver. They are primarily made up of cholesterol and can vary in size, ranging from a grain of sand to a golf ball. Gallstones can cause pain, inflammation, and other complications, leading to significant discomfort and disruption in daily life.
Myth 1: Only Older People Get Gallstones
Contrary to popular belief, gallstones are not limited to older individuals. While age is a risk factor, gallstones can affect people of all ages, including children and young adults. Various factors, such as genetics, obesity, hormonal changes, and rapid weight loss, can contribute to the development of gallstones, irrespective of age.
Myth 2: Gallstones Only Cause Abdominal Pain
While abdominal pain is a common symptom of gallstones, it is not the only manifestation. Gallstones can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, bloating, indigestion, and even back pain. In some cases, gallstones may lead to more severe complications, such as gallbladder inflammation or blockage of the bile ducts.
Myth 3: Gallstones Can Be Dissolved Naturally
There is a myth that gallstones can be dissolved naturally through home remedies or alternative therapies. While certain lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, may reduce the risk of developing new gallstones, they cannot eliminate existing ones. Once gallstones have formed, medical intervention is usually necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Myth 4: Surgery Is the Only Treatment Option
While surgery, specifically gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), is a common treatment for gallstones, it is not the only option. Depending on the severity and symptoms, healthcare professionals may recommend non-surgical approaches, such as medications to dissolve gallstones or advanced techniques like shock wave lithotripsy. The appropriate treatment plan varies for each individual and should be determined by a healthcare professional.
Myth 5: Gallstones Are Always Visible on Imaging Tests
Although imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scan are commonly used to diagnose gallstones, they are not foolproof. In some cases, gallstones may be too small to be detected or obscured by other structures, leading to false-negative results. Thus, a comprehensive evaluation by a medical professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Myth 6: Gallstones Can Turn into Cancer
Gallstones themselves do not turn into cancer. However, long-standing gallstones can lead to chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, a condition known as cholecystitis. In rare cases, prolonged inflammation can increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer. It’s important to manage gallstones promptly to minimize complications but be aware that cancer is not a direct outcome of gallstones.
Myth 7: Gallstones Are Caused by Eating Fatty Foods
While a high-fat diet may contribute to gallstone formation, it is not the sole cause. Other factors, such as genetics, hormonal imbalances, and rapid weight loss, play significant roles as well. It’s important to adopt a balanced diet and maintain a healthy lifestyle overall to reduce the risk of gallstone development.
Myth 8: Gallstones Can Be Prevented Completely
Preventing gallstones entirely is not always possible, especially for individuals with certain risk factors that are beyond their control. However, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing gallstones. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, and avoiding rapid weight loss or fad diets.
Myth 9: Gallstones Always Cause Symptoms
Not all gallstones cause noticeable symptoms. Some people may have gallstones without experiencing any pain or discomfort. These asymptomatic gallstones are often discovered incidentally during medical imaging tests conducted for unrelated reasons. However, even without symptoms, gallstones can still pose a risk of complications and should be monitored by a healthcare professional.
Myth 10: Gallstones Will Go Away on Their Own
Unfortunately, gallstones do not typically resolve on their own without medical intervention. Once gallstones have formed, they tend to persist and may even worsen over time. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action based on individual circumstances.
Conclusion
Gallstones are a prevalent health condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age, weight, or gender. It is important to dispel the myths surrounding gallstones and provide accurate information to promote better understanding. If you suspect you may have gallstones or have any concerns, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
FAQs
- Are gallstones only found in the gallbladder? No, gallstones can also be found in the bile ducts, which can cause blockage and other complications.
- Can I prevent gallstones by drinking a specific type of tea? There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that any specific type of tea can prevent gallstones.
- Are there any long-term complications associated with gallstones? Yes, if left untreated, gallstones can lead to serious conditions such as pancreatitis or cholecystitis.
Dr. Ahmed Raza, a renowned gastroenterologist with over 20 years of experience, is the dedicated founder of LifeWithNoGallbladder. With a passion for improving gallbladder health, Dr. Raza shares extensive insights, records, and guidance through his blog, providing individuals with the necessary information to make informed decisions.