Johnson's Head-to-Toe Gentle Tear-Free Baby & Newborn Wash & Shampoo, Sulfate-, Paraben- Phthalate- & Dye-Free, Hypoallergenic Wash for Sensitive Skin & Hair, 27.1 fl. Oz
28% OffIntroduction:
The Phrygian cap of the gallbladder, an interesting anatomical variation, holds sizeable importance in understanding gallbladder fitness. In this complete article, we will explore the importance of the gallbladder, introduce the concept of the Phrygian cap, and delve into its traits, incidence, formation, and functional implications. Additionally, we will examine diagnostic techniques, surgical considerations, potential complications, and ongoing research related to the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder.
The Anatomy of the Gallbladder:
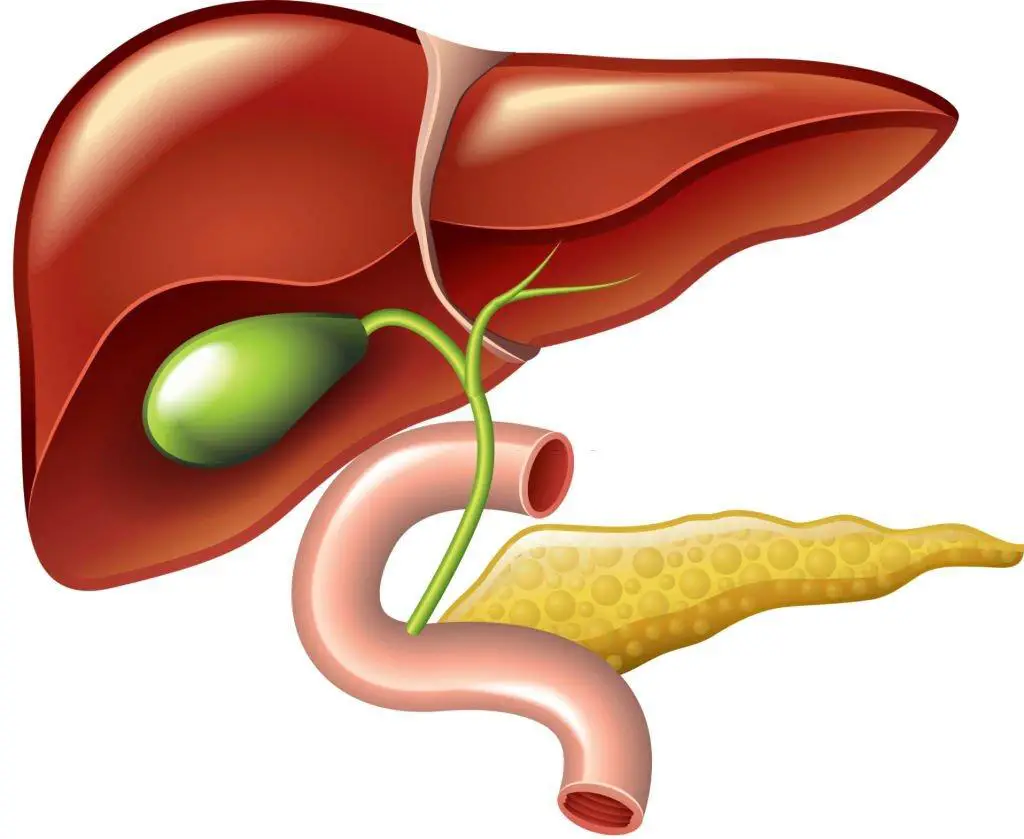
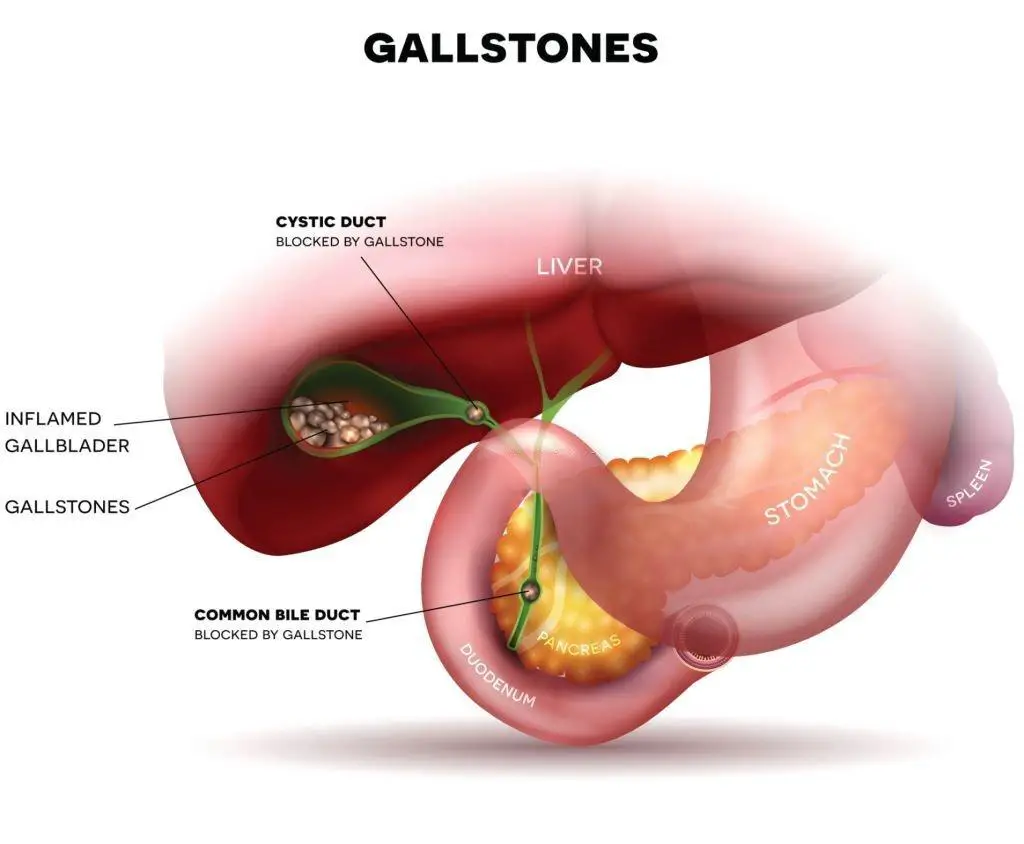
Before delving into the Phrygian cap, it’s miles vital to understand the anatomy of the gallbladder. Positioned below the liver, this pear-shaped organ performs a crucial role in the digestive system. It stores bile produced by the liver and releases it during digestion to aid in the breakdown of fats and the absorption of vitamins. The gallbladder’s features are crucial for maintaining a healthful digestive method.
Understanding the Phrygian cap:
The Phrygian cap is a unique anatomical configuration that alters the typical shape of the gallbladder. Its miles are characterized by a fold or bend at the fundus, such as the cap worn by Phrygian freedmen in ancient Rome. The superiority of the Phrygian cap varies among individuals, but its miles are typically considered an extraordinary anatomical variation.
Functional Implications of the Phrygian Cap:
The Phrygian cap of the gallbladder, even though typically an anatomical variation can also have capacity implications for gallbladder function and its association with sure gallbladder disorders. Whilst the Phrygian cap itself no longer directly affects the general function of the gallbladder, it may affect bile storage and launch and probably contribute to the development of gallbladder-associated situations.
1. Bile garage and launch: The gallbladder’s number one feature is to save and pay attention to bile produced by the liver until it is needed for digestion. The Phrygian cap no longer drastically affects the gallbladder’s ability to keep bile. However, due to the altered shape and potential variations in the gallbladder’s anatomy associated with the Phrygian cap, the discharge of bile can be affected to a point. The fold or bend in the gallbladder can also create a type of mechanical surroundings, doubtlessly influencing the efficiency and timing of bile release throughout digestion.
2. Affiliation with Gallbladder issues: while the Phrygian cap itself isn’t directly related to the development of gallbladder disorders, its presence can be related to positive situations. For instance, there have been observations suggesting a capacity correlation between the Phrygian cap and gallstone formation. Gallstones are solid deposits that could increase in the gallbladder due to the accumulation of LDL cholesterol or bilirubin. The altered gallbladder shape associated with the Phrygian cap can make contributions to modifications in bile float, probably affecting the hazard of gallstone formation.
Moreover, the Phrygian cap can be related to gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis) or other gallbladder issues. The altered anatomy and capacity adjustments in bile glide may also growth the chance of bile stasis, main to an increased susceptibility to irritation and related signs and symptoms.
It is important to be aware that similar studies are needed to set up a definitive causal courting among the Phrygian cap and gallbladder disorders. Contemporary knowledge indicates a capability association, however, extra research is required to elucidate the mechanisms and volume of this relationship.
In summary, whilst the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder itself no longer extensively affect gallbladder characteristics, it can affect the garage and release of bile. Moreover, it’s been related to an extended chance of gallstone formation and potential gallbladder inflammation. Destiny studies endeavors will shed greater light on the appropriate practical implications and institutions with gallbladder disorders, taking into account higher management and understanding of the Phrygian cap’s impact on universal gallbladder fitness.
Diagnostic Techniques for Phrygian Cap Identification:
To appropriately become aware of and diagnose the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder, several diagnostic strategies are employed. Those methods permit healthcare specialists to visualize and assess anatomical variation. The primary diagnostic tools used include ultrasound, MRI, and different imaging strategies.
1. Ultrasound: Ultrasound is a typically used diagnostic modality to assess the gallbladder and hit upon anatomical variations such as the Phrygian cap. It utilizes excessive-frequency sound waves to create actual-time photographs of the gallbladder and surrounding structures. Ultrasound permits the visualization of the gallbladder’s form, length, and any alterations in its ordinary anatomy. It is a non-invasive and price-powerful method, making it the desired preliminary imaging method for comparing the Phrygian cap.
2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides exact and excessive-resolution pix of the gallbladder and is useful for identifying the Phrygian cap. It uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate cross-sectional pictures of the body. MRI can provide better anatomical delineation and spatial facts, taking into consideration a complete evaluation of the gallbladder’s form and any variation’s gift, together with the Phrygian cap.
3. Computed Tomography (CT) test: CT scans can be hired to diagnose the Phrygian cap in sure instances. This imaging method uses X-rays and computer processing to generate certain cross-sectional photos of the gallbladder. CT scans can provide treasured records about the gallbladder’s shape, function, and any variation’s gift, inclusive of the Phrygian cap. However, because of using ionizing radiation and comparison dealers, CT scans are typically reserved for specific situations wherein extra facts are needed.
Demanding Situations and Boundaries in Diagnosing the Phrygian Cap:
Regardless of the availability of diverse diagnostic strategies, diagnosing the Phrygian cap can gift sure challenges and boundaries. These encompass:
1. Operator Dependency: The accurate identity of the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder is predicated on the expertise and experience of the deciphering healthcare expert. The translation of imaging research calls for thorough expertise in gallbladder anatomy and anatomical variations, along with the Phrygian cap.
2. Overlapping capabilities: The Phrygian cap will have overlapping functions with other gallbladder abnormalities or anatomical variations. Distinguishing the Phrygian cap from other conditions, such as gallstones or gallbladder polyps, can be tough, mainly in instances where more than one variation s or pathologies coexist.
3. Variability in Presentation: The Phrygian cap may additionally exhibit variable appearances and sizes, further complicating its identification. The fold or bend on the fundus can range from diffused to extra said, making it important to cautiously examine imaging findings to stumble on the Phrygian cap correctly.
4. Accessory Gallbladder: In uncommon times, an accessory gallbladder can be present, that can mimic the arrival of a Phrygian cap. Differentiating between an accent gallbladder and a Phrygian cap requires careful evaluation of the gallbladder’s form, place, and vascular supply.
No matter these demanding situations, the mixture of scientific assessment and imaging techniques, consisting of ultrasound and MRI, facilitates healthcare experts to diagnose the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder, bearing in mind appropriate control and affected person care.
Surgical Considerations and Treatment Options: when thinking about surgical methods regarding the gallbladder, the presence of the Phrygian cap calls for careful attention. Cholecystectomy, the surgical elimination of the gallbladder, may additionally require modifications or adjustments to accommodate the particular anatomy associated with the Phrygian cap. Surgeons should carefully evaluate the patient’s case to ensure the procedure is carried out with care and effectively.
In instances in which surgical removal of the gallbladder isn’t necessary, alternative remedy alternatives may be explored. Those alternatives may additionally include way-of-life changes, remedies, or management techniques tailored to the patient’s wishes.
Possible Complications and Risks Associated with the Phrygian Cap:
The Phrygian cap itself isn’t associated with inherent headaches. But, throughout surgical processes, such as cholecystectomy, the presence of the Phrygian cap may pose demanding situations or growth the danger of sure complications. For instance, the altered anatomy may also affect bile flow, making it important to make certain ok visualization and careful surgical approach to prevent complications inclusive of bile duct injury.
Additionally, people with this can have a comparable risk of growing gallstones, irritation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), or different gallbladder-associated situations. Ordinary monitoring and suitable preventive measures are vital for retaining gallbladder health in these individuals.
Research and Studies on the Phrygian Cap:
Scientific studies and studies have shed light on the Phrygian cap, imparting insights into its occurrence, characteristics, and ability implications. A few studies have aimed to decide the genetic and developmental elements contributing to the formation of the Phrygian cap. Others have explored its affiliation with gallbladder disorders, surgical results, and the impact on bile glide.
At the same time as giant development has been made, further research is needed to fully apprehend its implications and capability healing strategies to control associated conditions.
Summary Recapitulating the key points discussed in the article:
In summary, knowledge of the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder is critical for healthcare experts and individuals searching for insights into gallbladder health. Diagnostic strategies, surgical concerns, potential considerations, and ongoing research contribute to a comprehensive understanding of this anatomical variation. Live knowledgeable and conscious as we unveil the ultra-modern advancements and strive to beautify our expertise and management of the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1: what is the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder?
A: The Phrygian cap of the gallbladder is an anatomical variation characterized using a fold or bend on the fundus, comparable to the cap worn with the aid of Phrygian freedmen in historical Rome.
Q2: Is the Phrygian cap a common anatomical variant?
A: The Phrygian cap is typically considered a rare anatomical variation. Its prevalence varies among people, and it isn’t commonly encountered.
Q3: Does the Phrygian cap affect gallbladder features?
A: The Phrygian cap itself does now not drastically affect gallbladder features. However, due to the altered anatomy, it can have an impact on bile storage and release. It’s far crucial to note that the ideal practical implications are still being studied.
Q4: Can the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder reason any symptoms?
A: In most cases, the Phrygian cap no longer reasons particular signs. But, if associated with gallstones or irritation, signs inclusive of stomach ache, nausea, and indigestion may additionally arise.
Q5: How is the Phrygian cap recognized?
A: Diagnostic strategies, consisting of ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans, are typically used to visualize and diagnose the Phrygian cap. These imaging techniques allow healthcare experts to evaluate the gallbladder’s shape and pick out any anatomical variations.
Q6: Is the Phrygian cap associated with a multiplied threat of gallstones?
A: While the affiliation between the Phrygian cap and gallstones isn’t always completely understood, there had been observations suggesting a potential correlation. The altered anatomy and capacity modifications in bile waft may additionally contribute to an extended risk of gallstone formation. However, further research is needed to set up definitive dating.
Q7: Can the Phrygian cap of the gallbladder be surgically corrected?
A: Generally, the Phrygian cap itself does no longer require surgical correction unless it’s far inflicting extensive signs and symptoms or is associated with different gallbladder abnormalities. Surgical intervention, consisting of cholecystectomy (elimination of the gallbladder), can be taken into consideration if there are extra warning signs for surgical procedures.
Q8: Are there any preventive measures for people with the Phrygian cap?
A: There aren’t any particular preventive measures for individuals with the Phrygian cap itself. However, keeping a healthy lifestyle, which includes a balanced food regimen and everyday workout, can help promote overall gallbladder health and decrease the danger of associated situations.
Dr. Ahmed Raza, a renowned gastroenterologist with over 20 years of experience, is the dedicated founder of LifeWithNoGallbladder. With a passion for improving gallbladder health, Dr. Raza shares extensive insights, records, and guidance through his blog, providing individuals with the necessary information to make informed decisions.