Gut health plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. A healthy gut contributes to proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and a strong immune system. However, factors like poor diet, stress, and medication can disrupt the delicate balance of our gut microbiota, leading to digestive issues and various health problems. Fortunately, there are several natural methods you can adopt to heal your gut naturally and restore its optimal functioning. In this article, we will explore effective strategies for improving gut health and enhancing your overall vitality.
Introduction: Understanding Gut Health
The gut, also known as the gastrointestinal tract, is a complex system responsible for the digestion and absorption of food. It houses trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microorganisms play a vital role in maintaining gut health and influencing various aspects of our well-being, including metabolism, immune function, and mental health.
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut
Identifying the signs of an unhealthy gut is crucial for taking appropriate measures to restore its balance. Common symptoms of an unhealthy gut include bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, food intolerances, frequent infections, fatigue, and mood swings. If you experience these symptoms regularly, it may indicate an imbalance in your gut microbiota
Adopting a Healthy Diet
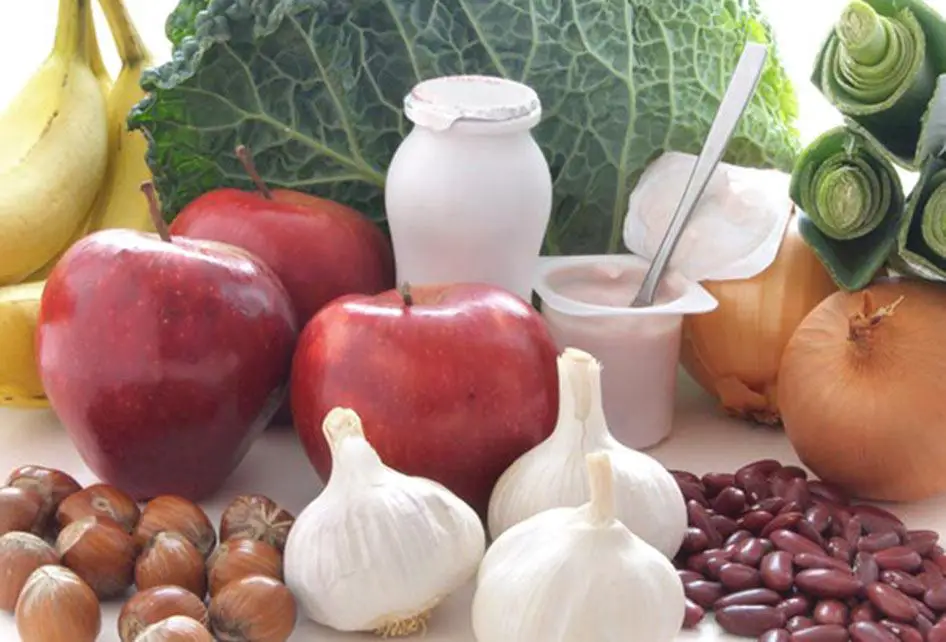
A healthy diet forms the foundation for gut health. Focus on consuming a wide variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporate foods rich in fiber, such as legumes, nuts, and seeds, as they promote regular bowel movements and support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. and to heal the gut
Incorporating Probiotics and Fermented Foods
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore the balance of gut microbiota. You can introduce probiotics into your system by consuming fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi. These foods provide live cultures of beneficial bacteria, which can enhance gut health and improve digestion.
Managing Stress Levels
Stress can have a significant impact on gut health. Chronic stress disrupts the balance of gut bacteria and compromises the integrity of the intestinal barrier. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and spending time in nature can help alleviate stress and promote a healthier and healing gut.
Getting Sufficient Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for overall well-being, including gut health. Lack of sleep can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and increase the risk of digestive issues. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to support optimal gut function and promote healing.
Regular Exercise for Gut Health
Regular physical activity benefits gut health in multiple ways. Exercise helps stimulate bowel movements, reduces inflammation, and promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, most days of the week to support a healthy gut.
Avoiding Toxins and Harmful Substances
Toxic substances like alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and harm the gut lining. Limit or avoid the consumption of these substances to protect your gut health. Additionally, minimize exposure to environmental toxins by choosing organic and natural products whenever possible.
Hydration and Gut Health
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining a healthy gut. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps prevent constipation and supports the transport of nutrients throughout the digestive system. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day and increase your intake during hot weather or physical activity.
The Role of Fiber in Gut Health
Fiber is a crucial component of a gut-healthy diet. It acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. Increase your fiber intake by incorporating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes into your meals. However, it’s important to gradually increase fiber consumption to avoid digestive discomfort.
Mindful Eating and Gut Health
Practicing mindful eating can significantly improve gut health. Slow down and pay attention to your food, chewing thoroughly and savoring each bite. Avoid distractions like screens while eating and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Mindful eating promotes proper digestion and allows you to tune in to your body’s needs.
Natural Supplements for Gut Healing
Certain natural supplements can support gut healing and restore the balance of gut microbiota. Probiotic supplements provide concentrated doses of beneficial bacteria, while digestive enzymes aid in the breakdown of food. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate supplements for your specific needs.
Reducing Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics, while necessary in certain situations, can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. Whenever possible, explore alternative treatments or natural remedies before resorting to antibiotics. If you need to take antibiotics, discuss with your healthcare provider ways to minimize their impact on your gut health.
Healing the Gut through Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is a dietary practice that involves cycling between periods of fasting and eating. This approach allows the gut to rest and promotes the regeneration of the gut lining. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting intermittent fasting to ensure it is suitable for you.
1. Remove
Expunge the negative. The objective is to eradicate elements that have an adverse impact on the gastrointestinal (GI) environment, such as inflammatory edibles, infections, and gastric irritants like alcohol, caffeine, or medications. Inflammatory foods like gluten, dairy, corn, soy, eggs, and sugar can lead to food sensitivities. To identify any problematic foods, I recommend undertaking an Elimination Diet and undergoing IgG food sensitivity testing. Infections may arise from parasites, yeast, or bacteria. A comprehensive analysis of stool samples is crucial to assess the levels of beneficial bacteria and detect any prevailing infections. Treating the infections may involve herbal remedies, anti-parasitic drugs, antifungal medications, or even antibiotics.
2. Replace
Introduce the positive. Restore the essential components necessary for proper digestion and absorption that may have been depleted due to dietary factors, medications (such as antacids), illnesses, or the aging process. This entails incorporating digestive enzymes, hydrochloric acid, and bile acids, which are vital for adequate digestion.
3. Reinoculate
Reestablishing a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria is pivotal. This can be achieved by consuming a probiotic supplement containing strains like bifidobacteria and lactobacillus species. I recommend a daily dosage ranging from 25 to 100 billion units. Additionally, taking a prebiotic supplement (providing nourishment for beneficial bacteria) or consuming foods rich in soluble fiber is crucial.
4. Repair
Supplying the necessary nutrients to facilitate gut healing is essential. One of my preferred supplements is L-glutamine, an amino acid that promotes the rejuvenation of the gut lining. Other vital nutrients include zinc, omega-3 fish oils, and vitamins A, C, and E, along with beneficial herbs like slippery elm and aloe vera.
Conclusion
Prioritizing gut health is essential for overall well-being. By adopting a healthy diet, managing stress levels, getting sufficient sleep, and incorporating gut-healing strategies, you can restore the balance of your gut microbiota and improve your digestive health. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice, and listen to your body’s needs throughout the healing process.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Can I take probiotics and antibiotics together?
While it’s generally safe to take probiotics and antibiotics together, it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice. Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, including beneficial bacteria. Taking probiotics during or after a course of antibiotics can help replenish the beneficial bacteria and reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated digestive issues, such as antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Your healthcare provider can guide you on the timing, dosage, and specific strains of probiotics that may be most beneficial for you.
- Is intermittent fasting suitable for everyone?
Intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions or specific dietary needs. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting intermittent fasting to determine if it’s appropriate for you. Certain groups, such as pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with a history of eating disorders, or those with unstable blood sugar levels, may need to approach intermittent fasting with caution or avoid it altogether