1. Introduction
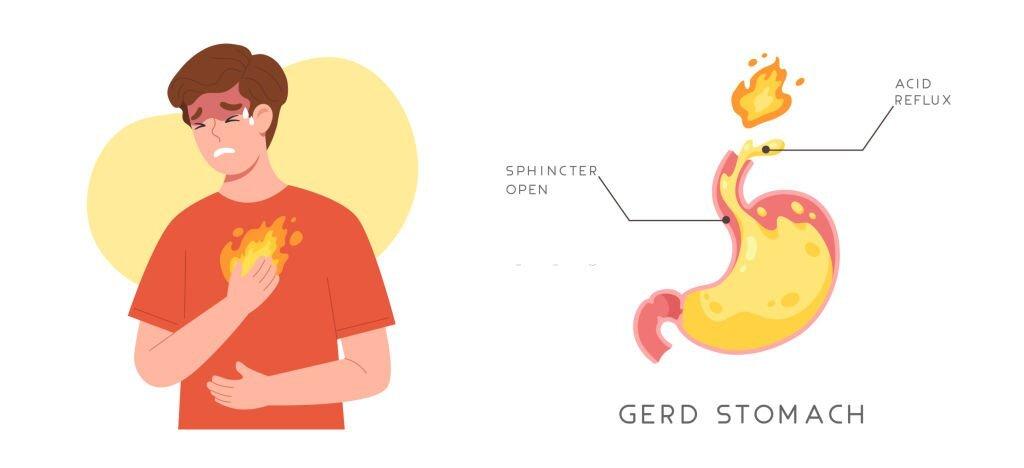
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD), also known as acid reflux, is a condition characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the oesophagus. It can cause discomfort and various symptoms that may significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of GORD, its symptoms, and available treatment options.
2. Understanding Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD)
GORD occurs when the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), a muscular ring that acts as a valve between the oesophagus and the stomach, weakens or relaxes inappropriately. This relaxation allows stomach acid to flow back up into the oesophagus, leading to irritation and inflammation.
3. Common Symptoms of GORD
The symptoms of GORD can vary from person to person but commonly include:
H1: Heartburn
Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, is a classic symptom of GORD. It typically occurs after meals and can worsen when lying down or bending over.
H2: Regurgitation
Regurgitation refers to the backflow of stomach acid into the mouth or throat. It can cause a sour or bitter taste, and individuals may experience a feeling of food coming back up.
H3: Chest Pain
Chest pain associated with GORD can be mistaken for a heart attack. It often occurs after eating and may radiate to the neck, jaw, or arms.
H4: Difficulty Swallowing
Some individuals with GORD may experience difficulty or pain while swallowing, known as dysphagia. This symptom should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
4. Diagnosis of GORD
To diagnose GORD, healthcare providers may perform various tests, including:
- Upper endoscopy: A thin tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to examine the oesophagus and stomach.
- Ambulatory acid (pH) monitoring: A small device is placed in the oesophagus to measure acid levels over 24 to 48 hours.
- Barium swallow: X-ray imaging is used to visualize the oesophagus and detect abnormalities.
5. Lifestyle Changes to Manage GORD
Making certain lifestyle modifications can help alleviate GORD symptoms and reduce the frequency of acid reflux episodes. Some recommended changes include:
- Avoiding trigger foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine.
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Elevating the head of the bed while sleeping.
6. Medications for GORD Treatment
Several medications are available to manage GORD symptoms and reduce acid production. These include:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): These drugs reduce stomach acid production and promote healing of the oesophagus.
- H2 blockers: These medications decrease acid production and provide relief from heartburn.
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can neutralize stomach acid and provide temporary relief.
7. Surgical Options for GORD
In cases where lifestyle changes and medications are ineffective, surgical intervention may be necessary. Two common surgical procedures for GORD treatment are:
- Fundoplication: The upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the LES to strengthen it and prevent acid reflux.
- Linx device: A small, flexible ring of magnetic beads is placed around the LES to help keep it closed while allowing food to pass through.
8. Dietary Recommendations for GORD
Certain dietary modifications can help manage GORD symptoms. It is recommended to:
- Opt for low-fat foods and lean protein sources.
- Avoid eating large meals before bedtime.
- Consume smaller portions of meals throughout the day.
- Identify trigger foods and eliminate them from the diet.
9. Natural Remedies and Alternative Therapies for GORD
Some individuals may find relief from GORD symptoms through natural remedies and alternative therapies. These can include:
- Herbal remedies like chamomile or licorice root tea.
- Acupuncture to alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being.
- Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or yoga, to reduce stress.
10. Complications Associated with GORD
If left untreated, GORD can lead to complications such as:
- Oesophagitis: Inflammation and damage to the lining of the oesophagus.
- Stricture: Narrowing of the oesophagus due to repeated irritation and scarring.
- Barrett’s oesophagus: Changes in the cells lining the oesophagus, which can increase the risk of oesophageal cancer.
11. Managing GORD during Pregnancy
Pregnant women may experience GORD due to hormonal changes and pressure on the stomach. To manage GORD during pregnancy, it is advised to:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals.
- Avoid lying down immediately after meals.
- Elevate the upper body while sleeping.
- Consult a healthcare professional before taking any medications.
12. GORD in Infants and Children
GORD can also affect infants and children. Common signs and symptoms in this age group include:
- Frequent spitting up or vomiting.
- Irritability during or after feeding.
- Poor weight gain.
- Chronic cough or wheezing.
If GORD is suspected in infants or children, it is crucial to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and management.
13. FAQs
- What causes Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD)?GORD is primarily caused by a weakened or relaxed lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), which allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Certain factors can contribute to this condition, including obesity, hiatal hernia, pregnancy, smoking, and certain medications.
- Can stress worsen GORD symptoms?While stress itself may not directly cause GORD, it can exacerbate the symptoms. Stress can lead to an increase in stomach acid production and may affect the functioning of the LES, making reflux symptoms more noticeable.
14. Conclusion
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD) is a prevalent condition characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the oesophagus. It can cause various uncomfortable symptoms and potentially lead to complications if left untreated. By understanding the symptoms and available treatment options, individuals with GORD can work with healthcare professionals to effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life.